Introduction to Compliance Management - old
Quick introduction to the module key capabilities
The Compliance Module is used to explain to people (inside and outside your organisation) how compliant your organisation is with any type of regulatory or contractual requirement.
The process begins by uploading free and open format (CSV-based) compliance packages (PCI, ISO, NIST, SOC2, SOX, etc.). The community has developed and maintains the most common packages used around the world in most industries. If you have to comply with something only you know, you can also make your own compliance packages in a CSV format and upload them to eramba.
Then you will link each requirement from that Compliance Package with other modules in eramba such as Internal Controls, Policies, Exceptions, Risks, Projects, etc. . The objective is that you will explain to eramba how you treat each one of these requirements.
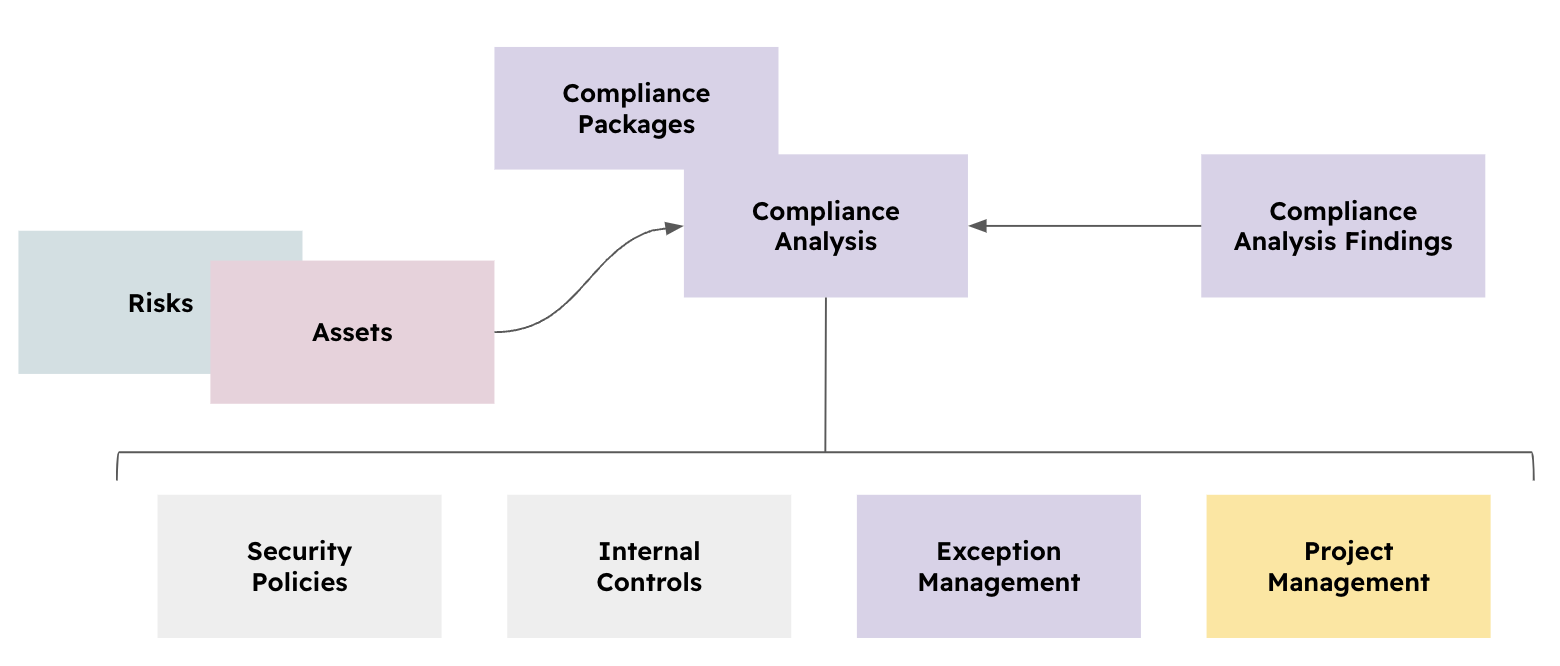
You can, optionally, link additional modules as well such as Risks and Assets. This might come in handy when dealing with specific regulations that require such links.
This allows you to record how your organisation decided to deal with each requirement, making it easy to demonstrate to auditors how you meet the requirements by simply viewing the related items. If the auditor needs more details a shortcut provides you direct access to the related items.
Since every module (Policies, Internal Controls, Exceptions, Projects) has a status of its own you can tell how they are performing (Risks have reviews, Policies have reviews, Controls have Audits, etc.).
This is how you can tell, not just what solution you have for each compliance requirement, but also if those solutions are working or not. The state of each solution item is displayed in the status column as shown in the screenshot above. Compliance requirements inherit the status of their solutions making it pretty clear to know when something is ok or not.
For example, for requirement 1.1.6 there is a solution in the form of an Internal Control that has not been tested on time. For that reason, the status of that requirement has a yellow label "Control Last Audit Expired".
This well-proven approach uses different charts to show how well your organisation is complying with any set of requirements and how that has changed over time.
Collecting reviews, audits, etc. using Eramba’s built-in notifications will ensure you have evidence ready for your auditors to review. It will also show when you do not have the evidence as well! You no longer need to review your compliance a month or two before the audit, the audits built into eramba help ensure you are compliant throughout the year.
You can upload mappings in between compliance packages if you wish, for example: whatever treatment is associated with PCI 1.3.4 automatically also applies to CIS 5.6.7.
As with any module in eramba, you can use filters, reports and notifications to collect status from teams across your organisation and ensure you never miss a deadline.
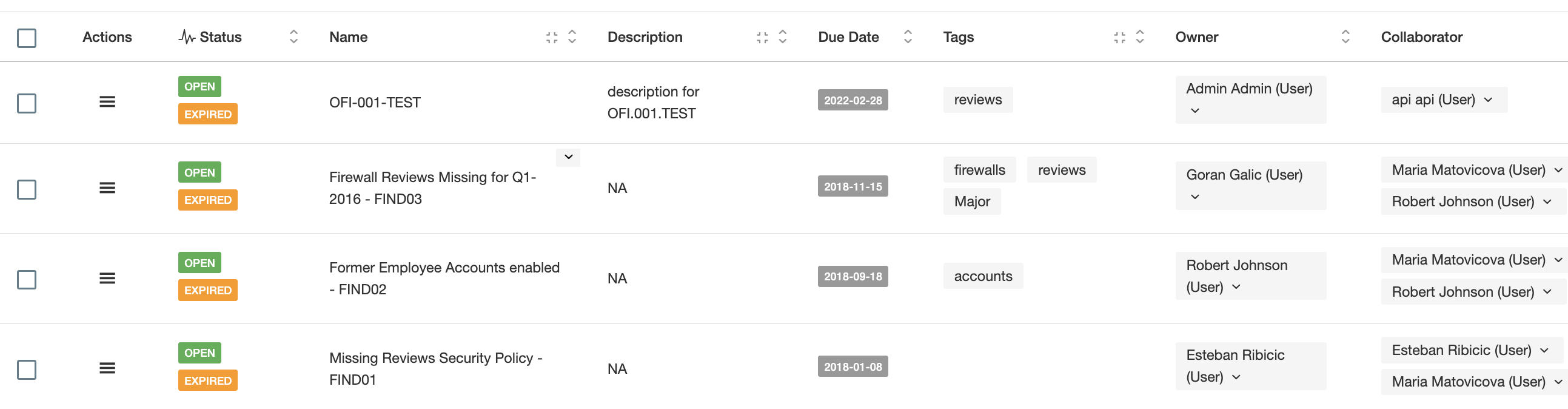
When your auditor comes and finds something you will be able to track down those findings in the form of Compliance Analysis Findings. This module allows you to assign findings to people, set deadlines and of course use notifications and reports to follow up on their status.
Playlist
- Episode 1Start Here1 min left
- Episode 2Introduction to Risk Management - old13 mins left
- Episode 3Introduction to Compliance Management - old16 mins left
- Episode 4Introduction to Data Privacy1 min left
- Episode 5Introduction to Incident Management7 mins left
- Episode 6Introduction to Online Assessments11 mins left
- Episode 7Introduction to Awareness Programs1 min left